Clean and Lean
Nutrition for Fat Loss
In collaboration with Verde Nutrition Co.
Clean and Lean – Nutrition for Fat Loss is an in-depth toolkit for successful fat loss and breaks down the science of nutrition into practical applications for sustainable results.
We call it fat loss rather than weight loss because we’re not looking to reduce lean muscle mass, the goal is to reduce body fat.
You’ll be guided through the foundations of nutrition, the science of fat loss and how it applies to your training and recovery, the go-to guide of household staples for meal prep, and finally how to tie it all together through delicious and healthy meals.
You’ll also have access to five worksheets that address key topics and aspects of your fat loss journey, and how these nutritional principles may be tailored specifically to your lifestyle.
The following is a sample of what you can expect in Clean and Lean – Nutrition for Fat Loss
What are the food groups?
 There are 5 major food groups, which have been outlined in the diagram below taken from The Australian Guide to Healthy Eating. These food groups serve as a guide to what foods constitute each food group and also detail roughly how many serves of each group you need per day. These values are based on an average daily adult intake; therefore your health goals may require a slight change from these values, although they do serve as a great guide.
There are 5 major food groups, which have been outlined in the diagram below taken from The Australian Guide to Healthy Eating. These food groups serve as a guide to what foods constitute each food group and also detail roughly how many serves of each group you need per day. These values are based on an average daily adult intake; therefore your health goals may require a slight change from these values, although they do serve as a great guide.
Yellow: carbohydrate and grain-based foods.
Blue: meat, fish, poultry, seafood, eggs.
Purple: dairy products
Green: fruit and vegetables.
How many serves should I consume from each group?
1 serve is about:
1 serve is about:
1 serve is about:
1 serve is about:
1 serve is about
Macronutrients & micronutrients
 The food and drinks you consume on a day-to-day basis are made up of macronutrients and micronutrients. Macronutrients are nutrients that are needed in larger amounts and consist of carbohydrate, protein, fat and alcohol. These are the nutrients from which we derive energy in the form of kilojoules or calories, and each macronutrient carries a different amount of energy per gram.
The food and drinks you consume on a day-to-day basis are made up of macronutrients and micronutrients. Macronutrients are nutrients that are needed in larger amounts and consist of carbohydrate, protein, fat and alcohol. These are the nutrients from which we derive energy in the form of kilojoules or calories, and each macronutrient carries a different amount of energy per gram.
Micronutrients do not have energy value and consist of the vitamins (such as the B group and fat-soluble vitamins), minerals (iron, calcium, zinc etc.) and antioxidants that help support many metabolic processes in our bodies. These are needed in smaller amounts.
Meeting the necessary requirements for macronutrients and micronutrients is essential for the overall functioning and recovery of our body, and depending on the fat loss goal there are certain manipulations of the macronutrient ranges that can assist you in getting you where you want to go.
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate foods are your primary fuel source during high-intensity exercise and should be included on training days. Carbohydrate foods consist of wholegrain bread and cereals, rice and pasta, fruit and vegetables, and dairy products, and once digested they are broken down into sugars for you to burn.
When you eat carbohydrates, your body has enzymes that break them down into smaller sugars to be absorbed, and this causes a spike in a hormone called insulin. The rate at which these sugars are broken down to be absorbed is called the Glycaemic Index.
Carb foods that break down rapidly for absorption are high GI foods, such as white bread, honey and soft drinks, and those with a slower rate of breakdown are called low GI foods, such as wholegrain varieties of cereals and grains, apples and leafy green vegetables. Choosing wholegrain varieties increases your daily fibre intake and helps control the release of the sugars into the bloodstream leading to a steady energy flow throughout the day.
Protein
Protein foods should be consumed at all main meals and snacks, especially after a training session, given their role in contributing to feelings of fullness and supporting recovery.
Protein foods can either come from plant-based sources, including legumes, nuts and tofu, or from animal sources including meat, fish, poultry, dairy products and eggs. You should be aiming to consume approximately 20-40g protein at main meals and 10-30g for snacks (depending on body weight and activity levels), as this allows an effective distribution throughout the day to help curb those cravings when in an energy deficit.
Fat
Fats should be included in small amounts when focusing on fat loss, rather than completely avoiding them. Healthy fats, or unsaturated fats, have an important role in satiety, the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and contain anti-inflammatory properties. Foods such as oily fish are great for including at least 2-3 times per week, and other additions such as avocado, nuts, seeds and olive oil are great for including as a thumb-sized serving at main meals. Although unsaturated fats carry many benefits, they do contain the highest amount of energy per gram, therefore adhering to the serving size helps to minimize excess energy intake during an energy deficit.
Alcohol
Although we would normally associate macronutrients with health, alcohol too yields an energy factor of which is important to address when speaking about fat loss. When alcohol is consumed, our body cannot store it therefore it is a priority to be metabolised as soon as possible. When large volumes of alcohol are consumed, this can impede the recovery process and also disrupt sleep patterns, which can catalyse a chain of consequences not ideal for fat loss.
Furthermore, alcohol disturbs the stimulation of hunger hormones. This makes it very easy to overindulge in high-energy nutrient-poor foods, consequently pushing you closer to, if not over to a positive energy balance favourable for weight gain. Avoiding alcohol will assist in reducing calories in, however in some social scenarios it is important to celebrate, so opting for sparkling water as a mixer over a soft drink or a glass of champagne over a cocktail can help keep calories in low.
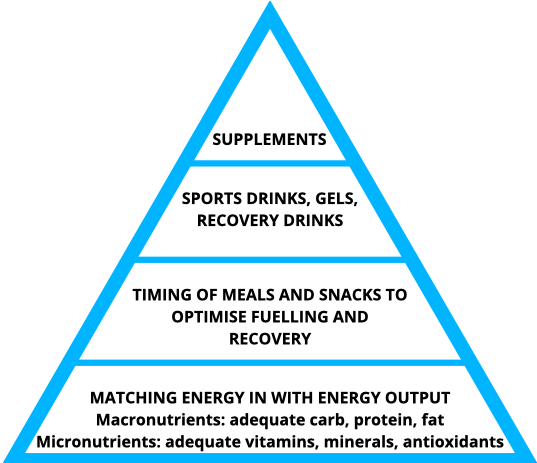
Ergogenic Aids & Supplements
With respect to nutrition, an ergogenic aid or supplement is any nutritional substance that has the capacity to improve physical performance or recovery due to the concentrated and isolated nature of a specific substance. When considering any supplement, there are three questions you should ask: is it safe? Is it legal? Is it effective? As evident in the pyramid above, supplements are the last thing to consider when it comes to your nutrition, as they’re there to supplement your nutritional and training plan, rather than be the plan.
Furthermore, if a supplement or ergogenic aid is indicated, it is imperative to consult an Accredited Sports Dietitian to provide advice around use and guidelines. Purchasing something online from another country may be subject to different regulation rules, therefore if competing there is an increased chance of inadvertent doping outcomes.
Worksheet: “Fundamentals Of Nutrition”
Yes!
Always seek the advice of your GP or Allied Health Professional (AHP) before embarking on any exercise program.
Running training is strenuous and tough on your body. You should make sure that you are physically healthy, getting enough sleep, and eating a nutritious diet before you begin. If you are currently fighting injury, this is probably not the time to begin your running training journey.
You can upgrade or cancel your subscription at any time, please discuss this with your coach.
If you are upgrading your subscription, please be mindful to do this just before your current subscription runs out.
If you need to cancel your subscription, please discuss this with your coach.
Contact the V&B Athletic team on 0414 932019 or hello@vandbathletic.com.au and one of us will be able to help!